 25-06-2023
25-06-2023- Blog
- 0 comments
- 5144 Views
Solid Wood:
Construction: Solid wood flooring is made entirely from solid pieces of wood. It is typically milled from a single plank of hardwood and is available in various thicknesses and widths
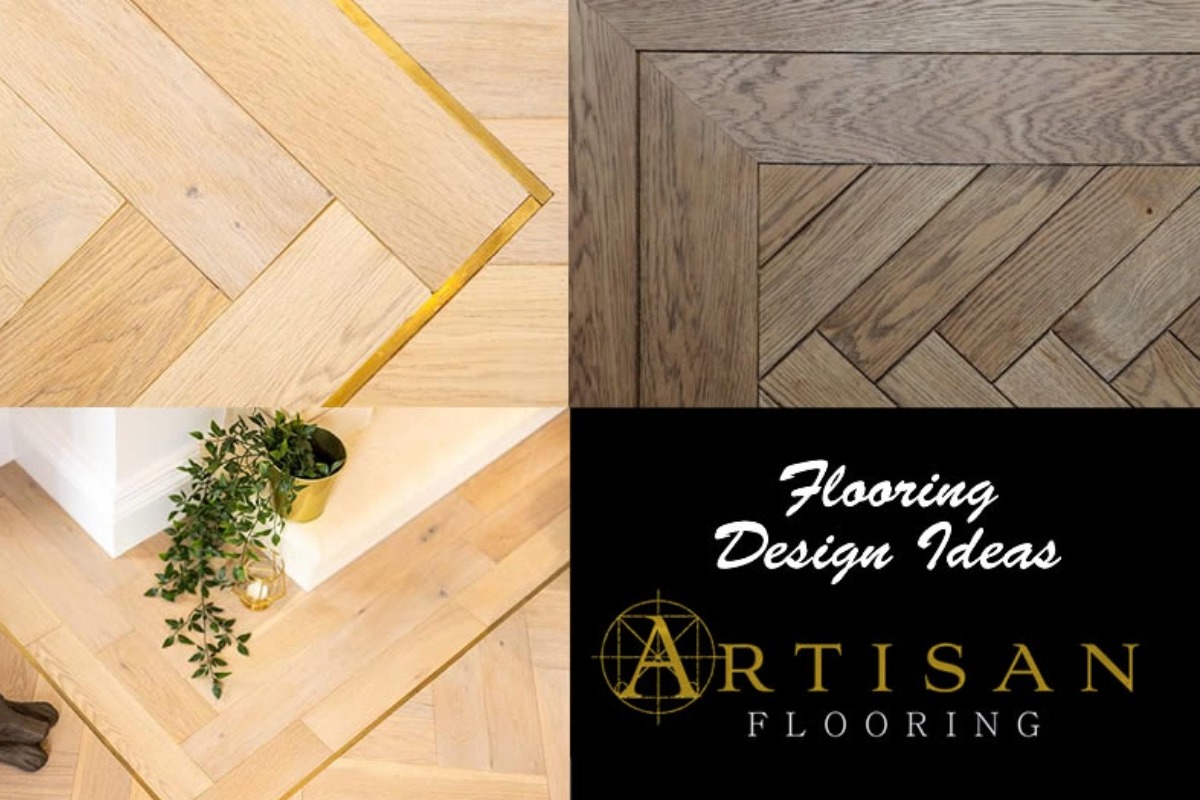
Authenticity: Solid wood offers the authentic look, feel, and natural variation of real wood. Each plank has unique grain patterns and textures, providing a timeless and organic aesthetic.
Durability: Solid wood is known for its durability and longevity. It can withstand heavy foot traffic, resist scratches and dents, and be sanded and refinished multiple times over its lifespan. Thicker solid wood planks have greater stability and can potentially last for generations.
Installation: Solid wood flooring is typically installed by nailing or stapling the planks directly to a wooden subfloor. It requires professional installation and is not recommended for installation directly over concrete or in below-grade areas.
Susceptibility to Moisture: Solid wood is more sensitive to moisture and humidity changes compared to engineered wood. It can expand or contract with fluctuations in moisture levels, leading to warping or gaps between the planks.
Engineered Wood:
Construction: Engineered wood flooring is constructed with multiple layers. It typically consists of a top layer (veneer) of real hardwood and several layers of plywood or high-density fiberboard (HDF) underneath. These layers are bonded together under heat and pressure.
Stability: The layered construction of engineered wood provides enhanced stability and resistance to moisture compared to solid wood. It is less prone to expansion, contraction, and warping, making it suitable for areas with fluctuating humidity levels or installations below grade.
Versatility: Engineered wood is available in a wide range of wood species, finishes, and plank sizes. It offers greater versatility in terms of installation options, including floating installation, glue-down, or nail-down methods. It can be installed over various subfloors, including concrete
Refinishing: The number of times engineered wood can be sanded and refinished depends on the thickness of the hardwood veneer layer. Thicker veneer layers allow for more refinishing cycles, while thinner ones may have limitations.
Environmentally Friendly: Engineered wood utilizes fewer hardwood resources compared to solid wood, making it a more environmentally friendly option. The use of fast-growing wood species for the inner layers also contributes to its sustainability.
Overall, solid wood offers unmatched authenticity and durability, while engineered wood provides enhanced stability, versatility, and better resistance to moisture. The choice between the two depends on factors such as personal preferences, installation requirements, budget, and the specific conditions of the space where the flooring will be installed.
















Recent Comments
No Comments have been left yet! Be the first :)